There are few kinds of structures as varied in their use – and as efficient to deploy – as prefabricated buildings. From industrial complexes to construction sites, energy plants or events worldwide, there’s often the need to get a structure that’s sturdy, secure, and set up fast – yet also easy to take away once its purpose has been served.
However, it would be remiss to disregard the possibilities of prefabricated buildings and their business applications so simply. In truth, the more business leaders and entrepreneurs explore the possibilities of prefabricated buildings, the more likely they are to encounter terminology, jargon and application potential that they might not find simple to understand.
Fortunately, gaining some deeper insight into how prefabricated buildings work – and where best to make use of them – need not be a complicated task. Today, we will explore what prefabricated buildings are, how they are put together, the benefits of using them and the applications you can take advantage of.
What are Prefabricated Buildings?
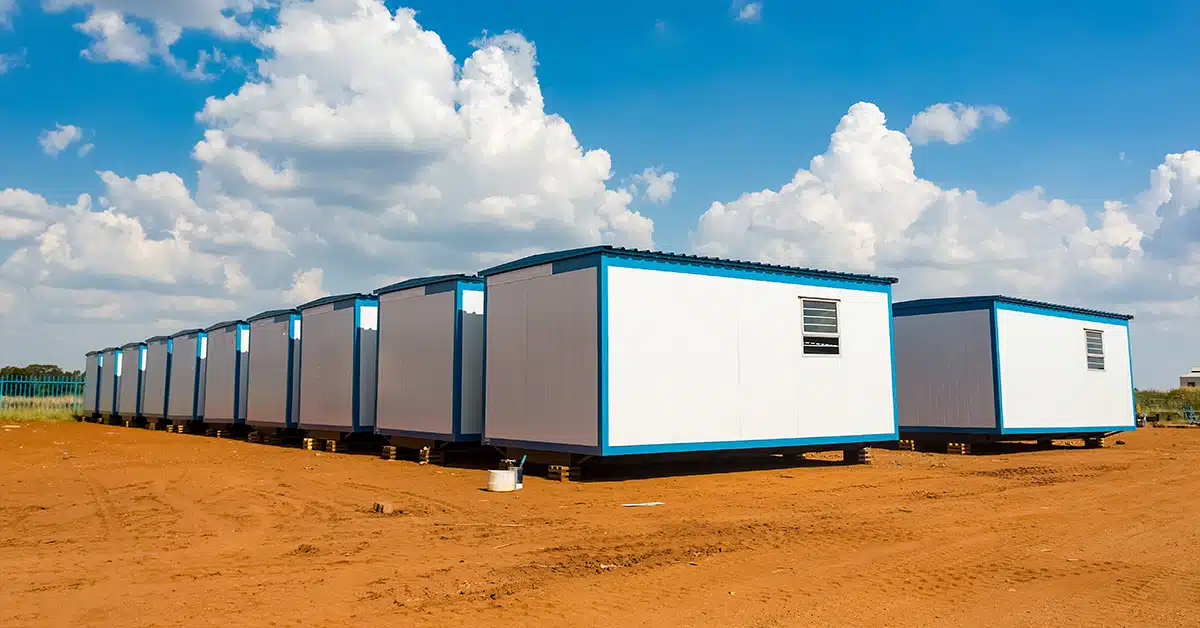
Prefabricated buildings, also known as ‘prefabs’, are highly efficient yet highly secure and sturdy structures. You have likely seen them countless times, perhaps without realizing – little huts at music events, a prefab building for the foreman on a construction site, and so on.
Active sites that change rapidly, such as oil & gas sites and construction projects, cannot rely on temporary structures like canvas tents to sustain security and safety. Yet the idea of such sites committing to fully building a structure simply to serve a purpose during the interval of the project is simply unrealistic and uneconomical.
This is where prefabs shine – yet they are far from their only use. As we will explore, there are several applications for prefabs, depending on your strategy – and they can be a semi-permanent addition to a given premises too, if the need arises.
How are Prefabricated Buildings Made?
Frequently, people who visualize prefabricated buildings picture corrugated metal sides or hardy plasterboard walls with little windows and a flat roof.
In fact, prefabs come in far more forms than that, and use plenty of different materials besides. It’s now possible to construct prefabricated buildings out of brickwork and hoist them into position via crane, for example.
Prefabricated buildings also often take advantage of ecological and circular economic thinking in how and why they are put together. For example, many prefabricated buildings are built out of modified shipping containers which have passed their service life – and thus go on to serve a far greater purpose than lying abandoned and ruining the environment.
What are the Benefits of Prefabricated Buildings?
The level of innovation that goes into prefabricated buildings today – both in design and in deployment – demonstrates their growing range of practical applications.
However, the core principles behind why entrepreneurs, businesses and heavy industries make such prevalent use of prefabricated buildings remains relatively unchanged.
Broadly speaking, the advantages can be summed up as follows:
Prefabricated buildings use space intelligently
On many industrial worksites, space is at a premium. Areas not occupied by vehicles, professionals hard at work or materials in need of storage and conveyance are few and far between.
Prefabricated buildings are designed to be compact – yet simultaneously spacious and with plenty of storage within.
Prefabricated buildings are cost-effective
Establishing a structure at any given operational site could be unfeasibly costly, were it not for prefabricated structures.
Whether folded out and erected onsite, or hoisted into place via crane or truck, prefabricated structures give tremendous flexibility for very little capital outlay.
Prefabricated buildings are sturdy and secure
Despite being relatively lightweight and simple to transport using most industrial equipment or vehicles, prefabs do not compromise on security or structural integrity either.
Most prefabricated structures can weather even the most imposing climate conditions, in some of the most demanding access sites and energy extraction projects around the world.
Similarly, their unassuming outward appearance and strong resilience to tampering means that the storage of valuables and assets within prefabricated buildings is always going to be safe from crime.
How Many Kinds of Prefabricated Buildings are There?
In truth, this is a figure that is likely to increase all the more as time goes on – innovations are happening in the prefab industry all the time.
However, the most commonly deployed and utilized prefabricated buildings today often stick to common structural best practices that make them efficient and reliable to use – while also matching the expectations and intended use-cases of their buyers.
Here are some popular examples of prefabricated buildings:
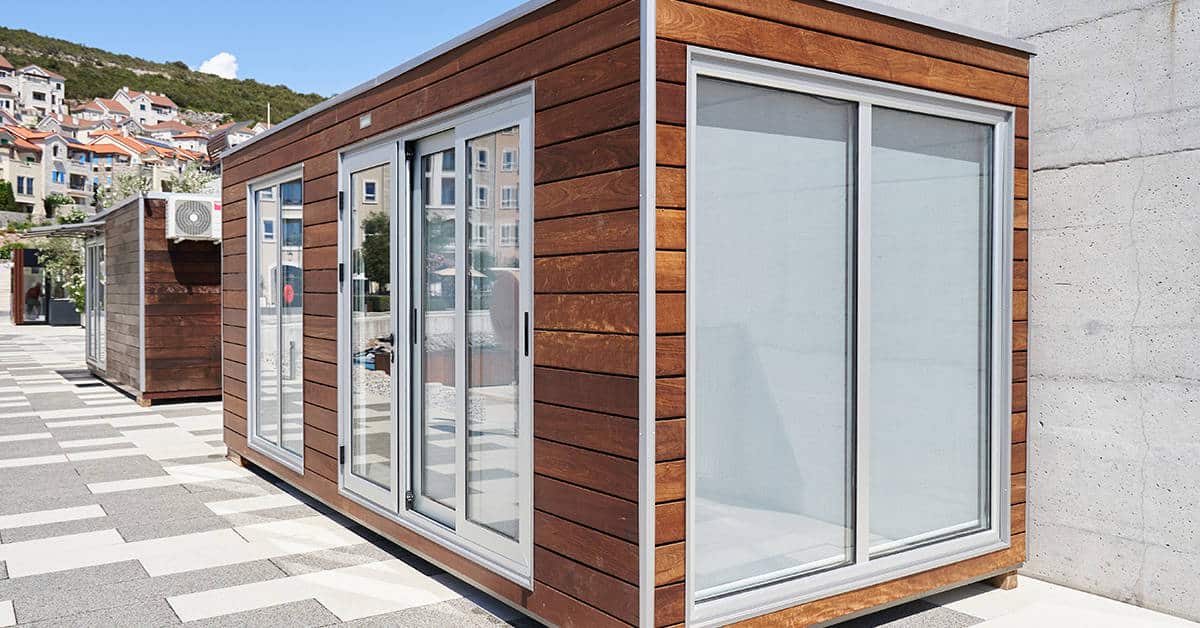
- Standard buildings: Versatile structures used for security booths, offices, and more.
- E-houses: Specifically designed for housing electrical equipment.
- Modular buildings: Customizable and expandable structures for various functions.
- Knock-down buildings: Ideal for sites with limited space.
- Modified shipping containers: Repurposed containers for diverse applications.
- On-site buildings: Constructed directly at the project location.
Which Industries Make Use of Prefabricated Buildings?
While prefabricated structures are active in a range of commercial applications today, their sturdiness, reliability and ease of deployment mean that industrial projects and intensive construction sites are where they are seen the most.
Here are some examples of where prefabs are able to add versatility and value to an ongoing industrial undertaking.
- Oil & gas projects: Providing secure and comfortable structures in remote locations.
- Data Centers: Ensuring efficient and reliable operation for critical IT infrastructure.
- Power Equipment: Protecting and managing essential power generation and distribution components.
Learn More About Prefabricated Buildings
The more you explore the possibilities and potential offered by prefabs, the more applications and use cases are certain to spring to mind for your latest industrial endeavors.
Understanding which is the best prefabricated building to use, under which circumstances and for what industrial application, is a nuanced undertaking – but not one in which you need to act alone.
Get in touch with our team today, and we will discuss the needs and expectations of your current industrial project – and advise on a solution that best fits the operations you have in mind.